©Copyright 2019 SIKO POLYMERS (SUZHOU) CO., LTD All rights reserved.Site Map Powered by iwonder.cn
- Email Uskevin@sikopolymers.com


Polyetherimide, referred to as PEI in English, Polyetherimide, with amber appearance, is a kind of amorphous thermoplastic special engineering plastic which introduces flexible ether bond (- Rmae Omi R -) into rigid polyimide long chain molecules.

The structure of PEI
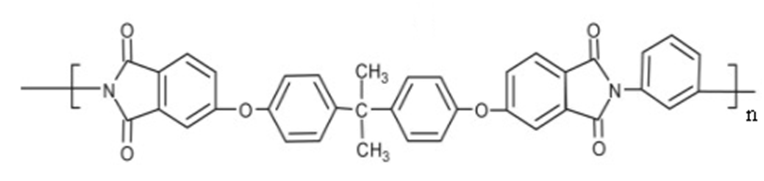
As a kind of thermoplastic polyimide, PEI can significantly improve the poor thermoplasticity and difficult processing of polyimide by introducing ether bond (- Rmurmurr R -) into the polymer main chain while retaining the ring structure of polyimide.
Characteristics of PEI
Advantages:
High tensile strength, above 110MPa.
High bending strength, above 150MPa.
Excellent thermo-mechanical bearing capacity, thermal deformation temperature greater than or equal to 200 ℃.
Good creep resistance and fatigue resistance.
Excellent flame retardancy and low smoke.
Excellent dielectric and insulation properties.
Excellent dimensional stability, low coefficient of thermal expansion.
High heat resistance, can be used at 170 ℃ for a long time.
It can pass through microwaves.
Disadvantages:
Contains BPA (bisphenol A), which limits its application in infant related products.
Notch impact sensitivity.
Alkali resistance is general, especially under heating conditions.
PEEK

PEEK scientific name polyether ether ketone is a kind of polymer which contains one ketone bond and two ether bonds in the main chain structure. It is a special polymer material. PEEK has a beige appearance, good processability, sliding and wear resistance, good creep resistance, very good chemical resistance, good resistance to hydrolysis and superheated steam, high temperature radiation, high thermal deformation temperature and good internal flame retardancy.
PEEK was first used in the field of aerospace to replace aluminum, titanium and other metal materials to make internal and external parts of aircraft. Because PEEK has excellent comprehensive properties, it can replace traditional materials such as metals and ceramics in many special fields. Its high temperature resistance, self-lubrication, wear resistance and fatigue resistance make it one of the most popular high-performance engineering plastics.
As a thermoplastic polymer material, the characteristics of PEI are similar to those of PEEK, or even the replacement of PEEK. Let's take a look at the difference between the two.
PEI | PEEK | |
Density (g/cm3) | 1.28 | 1.31 |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 127 | 116 |
Flexural Strength (Mpa) | 164 | 175 |
Ball Indentation Hardness (MPa) | 225 | 253 |
GTT(Glass-transition Temperature) (℃) | 216 | 150 |
HDT (℃) | 220 | 340 |
Long-term Working Temperature (℃) | 170 | 260 |
Surface Specific Resistance (Ω) | 10 14 | 10 15 |
UL94 Flame Retardant | V0 | V0 |
Water Absorption (%) | 0.1 | 0.03 |
Compared with PEEK, the comprehensive performance of PEI is more eye-catching, and its biggest advantage lies in the cost, which is also the main reason why some aircraft design materials are selected by PEI composite materials. The comprehensive cost of its parts is lower than that of metal, thermosetting composites and PEEK composites. It should be noted that although the cost performance of PEI is relatively high, its temperature resistance is not too high.
In chlorinated solvents, stress cracking occurs easily, and the resistance to organic solvents is not as good as that of semi-crystalline polymer PEEK. In processing, even if PEI has the processability of traditional thermoplastic engineering plastics, it needs higher melting temperature.